Jocker
Jocker is a Jolie service which provides a Jolie interface of the HTTP docker APIs. Thanks to Jocker it is possible to interact with a docker server just as it is a Jolie service. At this link it is possible to check the API supported by Jocker.
Jocker is available as a docker container, just type the following commands for activating a Jocker instance:
docker pull jolielang/jocker
docker run -it -p 8008:8008 --name jocker -v /var/run:/var/run jolielang/jocker
Important notes/
- Jocker is listening on the container internal port
8008, thus if you need to change it, just configure properly the container when running it using the parameter-p 8008:8008. - Jocker communicates with the docker server using the localsocket
/var/run/docker.sockas it is suggested by docker documentation. Thus, pay attention when creating the jocker container to share the host volume where such a socket is available by setting parameter-v /var/run:/var/run. - At the present Jocker is an experimental project, so use with cautions.
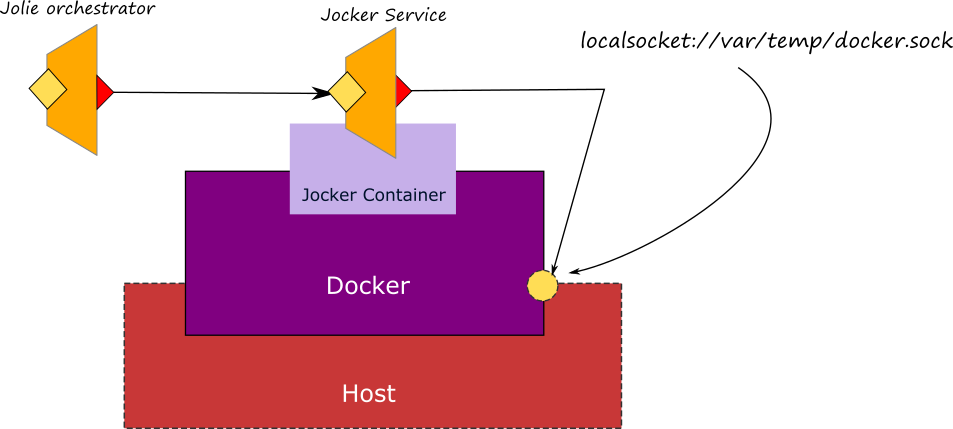
Once installed, it is possible to call Jocker as a usual Jolie service.
Example: creating a Jolie orchestrator for deploying a Jolie system into docker
In this example we show how to build a Jolie orchestrator which is able to deploy a Jolie system by exploiting the Jocker APIs. The full code of the example can be checked here.
In this example we aim at deploying the same system commented at section Basics/Composing Statements/Parallel altogether just executing a single orchestration jolie script. For the sake of brevity we grouped the three services into three different folders. At this link it is possible to navigate the three folders. Each folder contains all the necessary files for executing each single service, moreover it also contains the Dockerfile which defines how to deploy that specific service into docker as we explained in section Containerization/Docker/Create an image.
The code of the orchestrator can be evaluated here. Just try it running the following command:
jolie jockerOrchestrator.ol
The steps it implements are:
Creation of the system/
-
Creation of the docker images of the three services
build@Jocker(rqImg)(response); -
Creation of the network
testnetwhere connecting the containerscreateNetwork@Jocker( ntwCreate_rq )( ntwCreate_rs ); -
Creation of the three containers
createContainer@Jocker( cntCreate_rq )( cntCreate_rs ); -
Attaching each container to the network
testnetattachContainerToNetwork@Jocker( attachCnt2Ntw_rq )(); -
Starting of each container
startContainer@Jocker( startCnt_rq )(); -
Inspecting the container for checking it is running
inspectContainer@Jocker( inspect_rq )( inspect_rs );
Testing the system/
-
Invoking of the
infoServicefor testing if it is workinggetInfo@InfoService( { .city = "Rome" } )( info )
Disposing the system/
-
Stopping all the containers
stopContainer@Jocker( stopCnt_rq )(); -
Removing all containers
removeContainer@Jocker( stopCnt_rq )( ); -
Removing the network
testnetremoveNetwork@Jocker( ntwRemove_rq )(); -
Removing all the images
removeImage@Jocker( rmImage_rq )();